A course from Udemy I am taking it around January 2025 to refresh my memory about medical device industry. It is free with my companies educational budget
Introduction
ISO 13485 notes
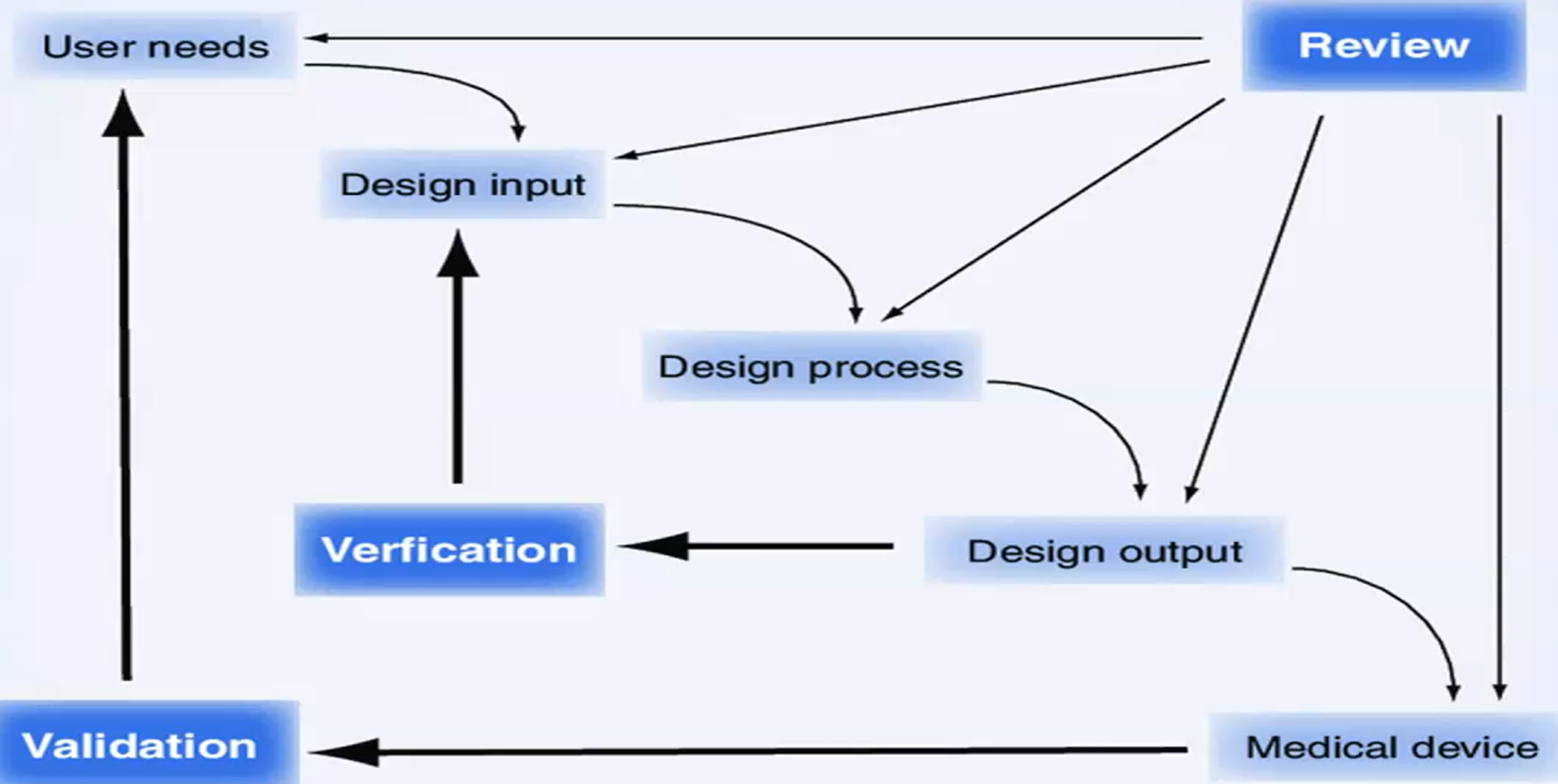
7.3.1 General
“The organization shall document procedures for design and development” “The organization shall plan and control the design and development of product. As appropriate, design and development planning documents shall be maintained and updated as the d&d progresses.”
7.3.2 Design and Development Planning
 who is responsible and authority for those steps?
IOVV matrix
resource needed, including necessary competence of personnel.
not documented, never happened!
“Shall” means must in ISO 13485 language.
who is responsible and authority for those steps?
IOVV matrix
resource needed, including necessary competence of personnel.
not documented, never happened!
“Shall” means must in ISO 13485 language.
Design and Development Inputs
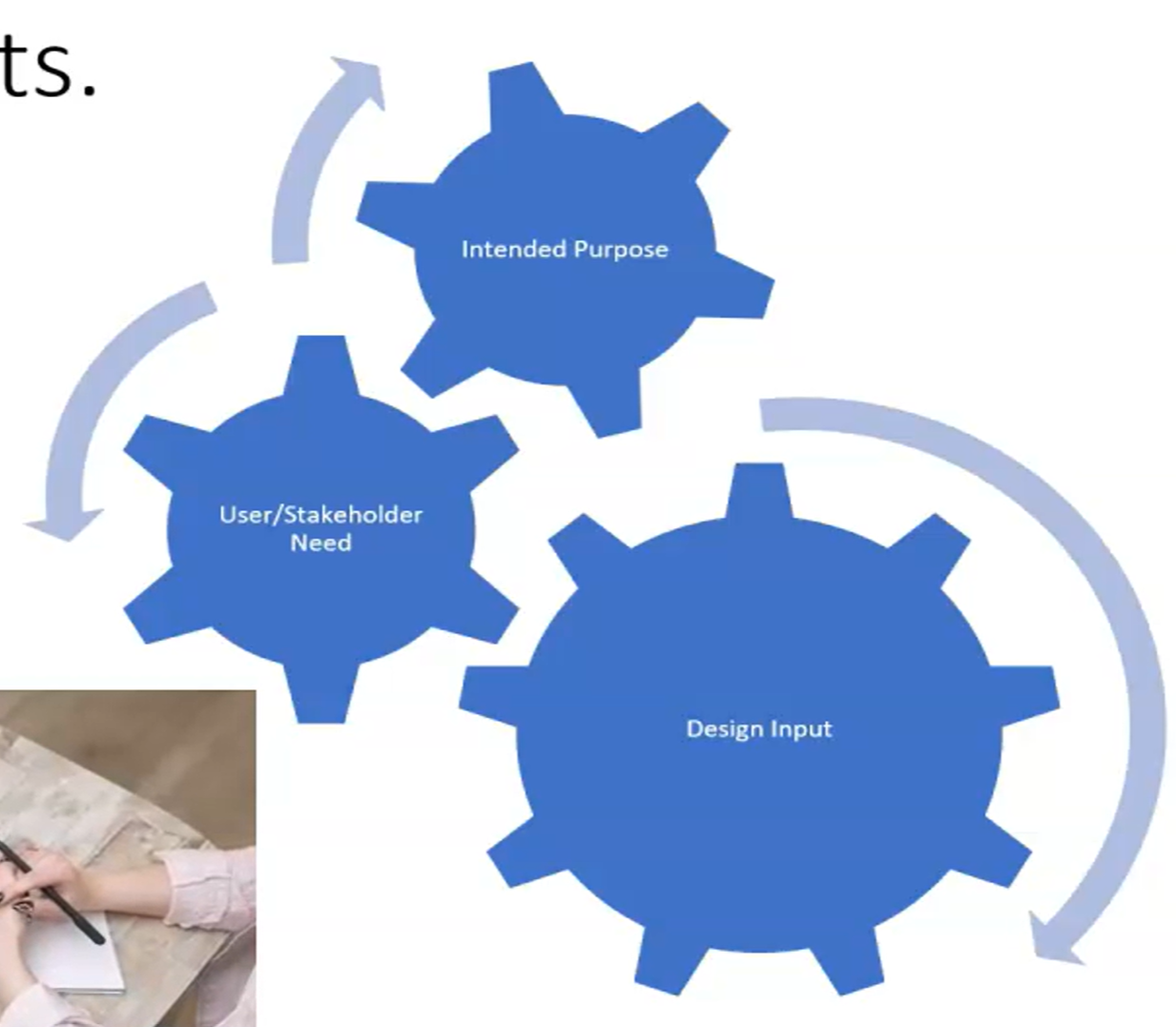
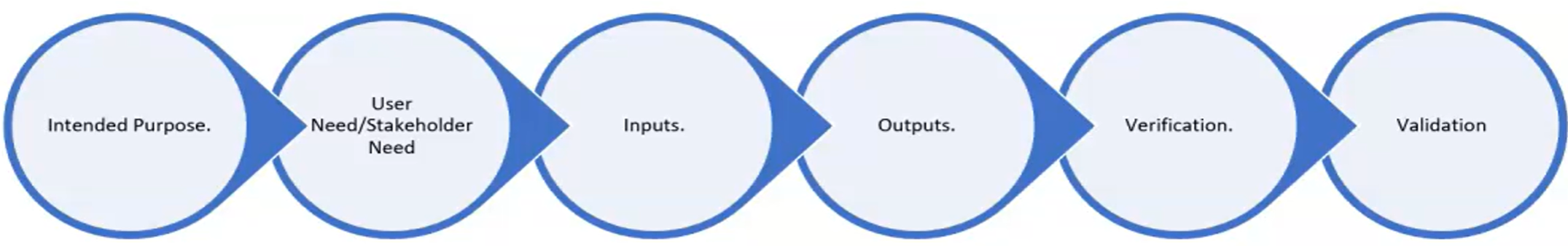
Intended Purpose Intended Purpose of Medical Device
7.3.3 Design and Development Inputs
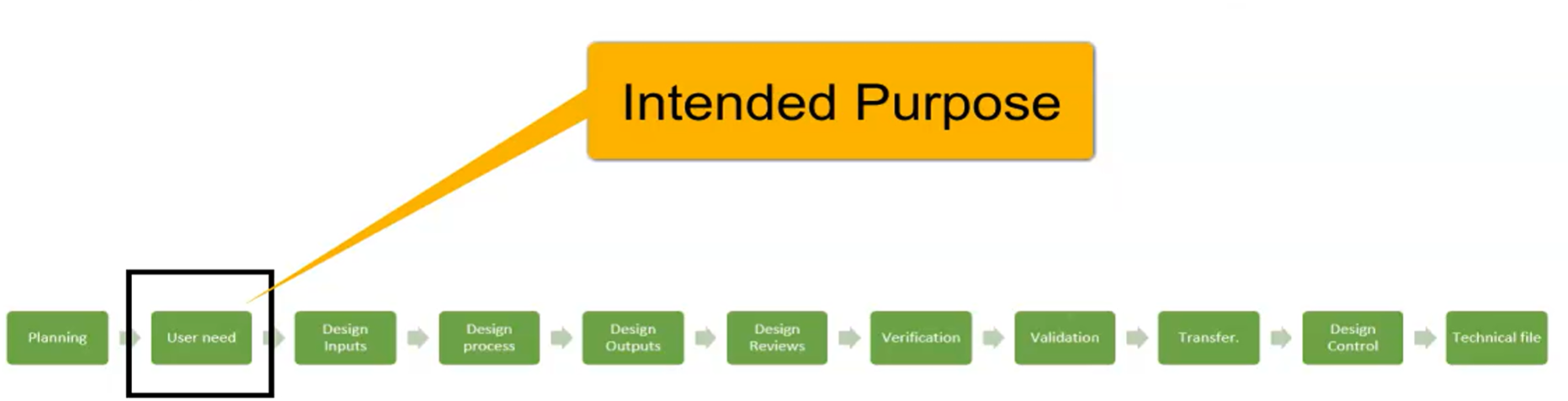 These inputs shall include:
“Inputs relating to product requirements shall be determined and records maintained”
a) functional, performance, usability and safety requirements, according to intended use.
Intended purpose definition from (MDR) Medical Device Regulation of EU:
These inputs shall include:
“Inputs relating to product requirements shall be determined and records maintained”
a) functional, performance, usability and safety requirements, according to intended use.
Intended purpose definition from (MDR) Medical Device Regulation of EU:
 intended purpose is the description of the medical problem that you want to address with your medical device.
Example: manufacturer wants to alleviate coronary artery disease with a drug eluting stent.
While Intended Purpose of Medical Device is describing “what is it”, Intended Use of Medical Device describes “how to use it”.
guide to intended purpose
intended purpose is the description of the medical problem that you want to address with your medical device.
Example: manufacturer wants to alleviate coronary artery disease with a drug eluting stent.
While Intended Purpose of Medical Device is describing “what is it”, Intended Use of Medical Device describes “how to use it”.
guide to intended purpose
- intended patient population
- device may exclude children or pregnant woman
- medical indication
- will state contradication. This means it will specify the disease the device will not treat.
- user
- lay person: a person without education of usage of medical device. Layperson in medical device design
- will the device be used by the layperson
- how to use it
- it is intended use. Where should the device should be used.
- Is invasive or non invasive
- How long should you use it
- creating the claims
- performance and benefit
- performance could be metal stent that can open coronary artery from 8mm to 32 mm in length
- benefit would be this allows to alleviate a coronary artery disease.
- risk vs benefit
- performance and benefit
User needs part1
- the first thing to understand is the user need.
- who is going to use the device?
- what do they need it for?
- what must it do?
- how fast?
- how will it be used?
- methods to obtain user needs
- current clinical protocols
- clinical risks/benefits
- concept drawings
- with user needs you are about to write Design Input of Medical Device Design input should be unambiguous.
User needs part2
- User need of Medical Device vs Design Input of Medical Device
- User need is:
- qualitative in nature
- User need is NOT:
- limiting the designer.
- product must be 120cm long
- scrutinize the why and what is the functional need.
- material choice
- limiting the designer.
- Translation into design input
- By asking why
- Determine a solution
- Translate user need to design input
- User need is:
User needs part3: customer
They can come from customer! End user vs customer. How to differentiate?
- Workshops, conferences, focus groups The doctor may not be the end user. They can be the last link. Nurses can comment about packaging, weight, color.
User needs part4: regulation
it can come from regulators! Compliance to regulation is generally obligation. Like MDR in europe. EMC compatibility or noise limitation can be user needs to design input. ISO standarts what labeling does the device need? like Unique identification, classification of device.
User needs part5: technical
Functional or technical requirements.
- What power or voltage goes into the medical device? 110V or 230V
- What loading may the device be loaded to?
- Temperature? Humidity?
- ergonomics, usability, machine interface, anthropometric data of users
User needs part6: performance
what the device does and how well should it do it?
User needs part7: sales
If you are selling a mobile ECG monitor, price should not exceed $120 selling price
User needs part8: manufacturing
For example clean room. It is very important to take their ideas at the beginning. Installation and calibration issues. Sterilization in packaging and manufacturing. Material supply and certification of components. Manufacturer suppose to be certified by ISO 13485
User needs part9: packaging and transportation
- what labelling is required. it may defer between US and EU
- Device trauma during transportation. Test it!
- Size of packaging should be fit into standard sizes
- Shelf life
User needs part10: environmental
They are now regulated.
- Can you recycle?
- Can it be reused?
- What about end of life management?
Design Inputs Design Input of Medical Device
Part 1
7.3.3 of the standart. Get qualitative user needs and translate them into quantitative design inputs a) functional, performance, usability and safety requirements, according to intended use b) applicable regulatory requirements and standards c) applicable output of risk management d) as appropriate, information derived from previous similar designs e) other requirements essential for design and development of the product and processes.
Part 2
Difference between “Shall” and “Should”
Design Input of Medical Device can be called design input, product requirements, technical requirements or design input requirements.
 Design input should be: clear, unambiguous, verifiable, objective, complete
Design input should be: clear, unambiguous, verifiable, objective, complete
- Answer to what
- Product requirement
- Design Input
- Answer to how
- Product specification
- design output To say device should be portable is not design input.
Examples



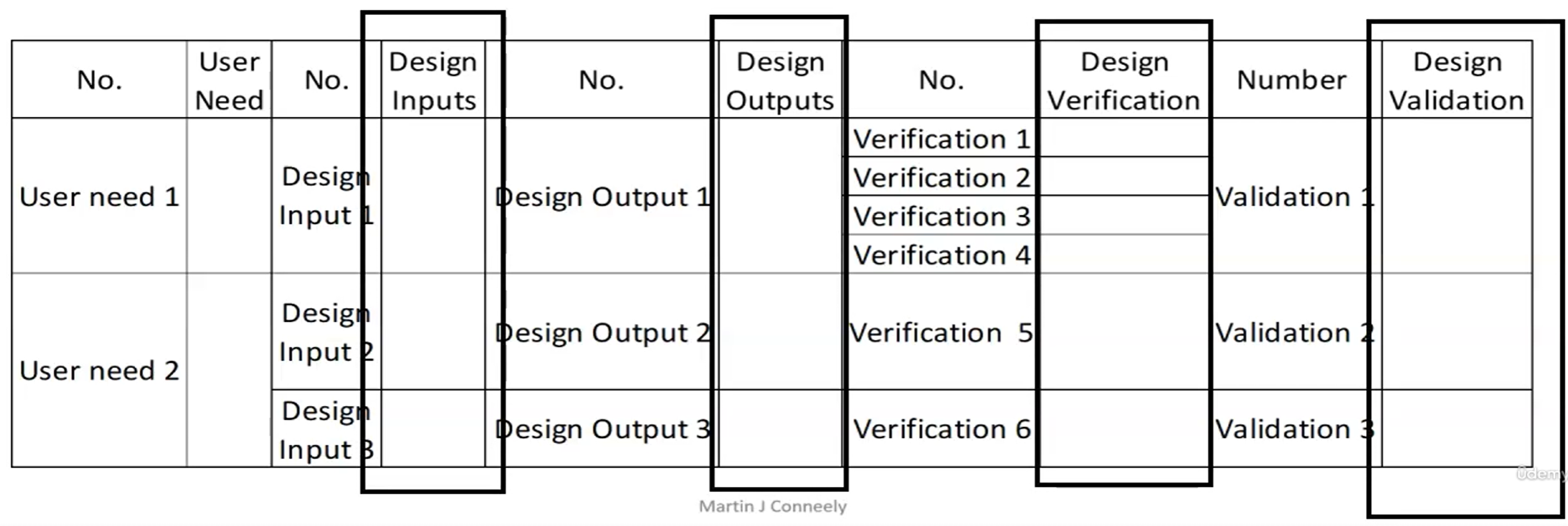
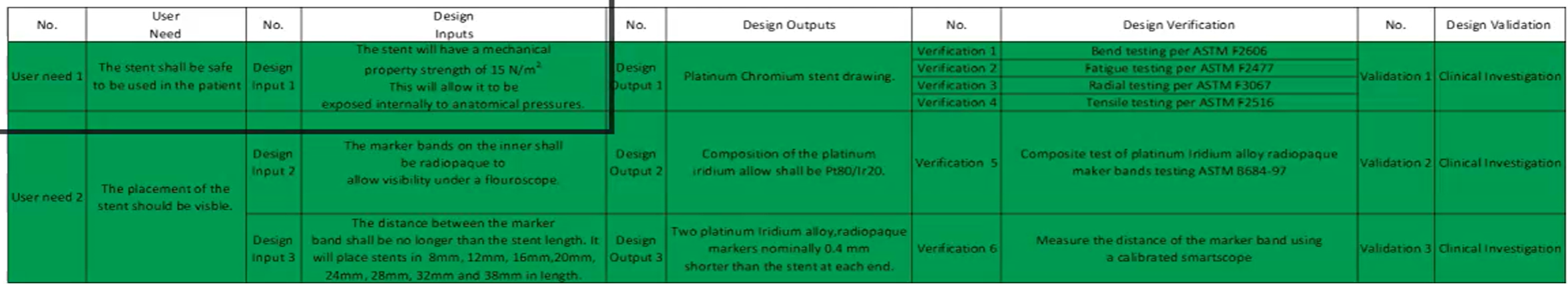
Part 3: Traceability
IOVV matrix
Risk Management of Medical Device
Acceptance Criteria of Medical Device
 Example of IOVV matrix:
Example of IOVV matrix:
 Introduce risk management as early as possible
Design input include acceptance criteria
Introduce risk management as early as possible
Design input include acceptance criteria
Part 4: Risk analysis
ISO 14971 Risk Management of Medical Device
-
The FDA requires risk assessments as part of design validation.
-
Design validation means establishing by objective evidence that device spesifications conform with user needs adn intended use
-
Since medical devices need to both safe and effective, risk management starts in the design phase, it is natural approach.
-
Records from risk management activities shall be maintained
-
The standard recomends ISO 14971 for guidance related to risk management
-
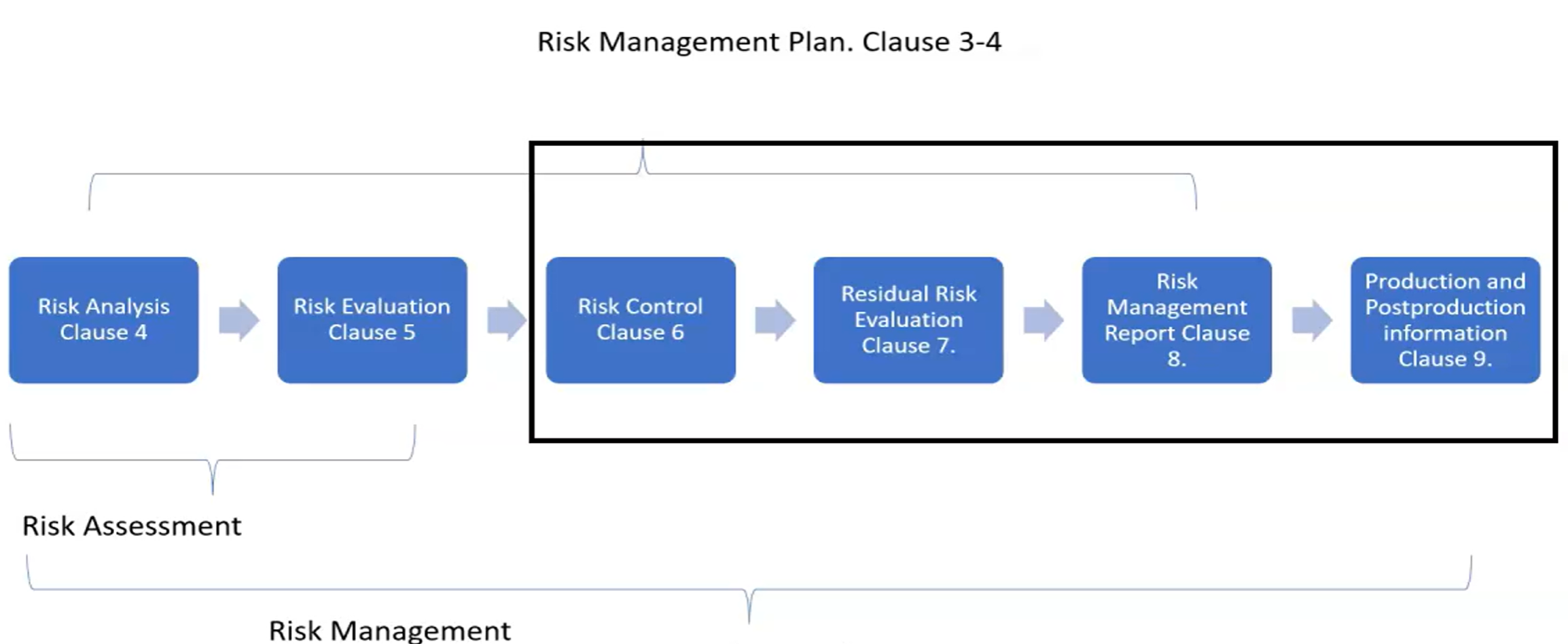
Risk management plan has standard elements:
- Scope ( including the life cycle )
- Responsibilities and authority
- Review requirements
- Risk acceptability criteria
- Risk verification
- Production activity data collection and review
- Post production activity data collection and review
Desing Outputs Design Output of Medical Device
Part 1
Section 7.3.4 of ISO 13485 a) It should meet the input requirements for design and development b) Provide appropriate information for purchasing, production and service provision c) Contain or reference product acceptance criteria d) Specify the characteristic of the product that are essential for its safe and proper use It should be clear, concise and. Verified version of design input “Records shall be maintained”
Part 2
(DMR) Device Master Record of Medical Device Technical File of Medical Device Design outputs are the how’s. Creating spesifications for the product. Design outputs can be:
- Drawing
- Material specs
- Inspection reports
- Service instructions
- MFG instructions
- Batch records
- Testing instructions
- Software code
- QA specs
- packaging labelling
Design and Development Review
Section 7.3.5 “At suitable stages, systematic reviews of design and development shall be performed in accordance with planned and documented arrangements to:” Has the design meet the user needs? b) identify and propose necessary actions. We need to document it!
- Any actions needs to be documented
- What design are you reviewing
- Who was involved
- Date it took place
Verification Verification of Medical Device
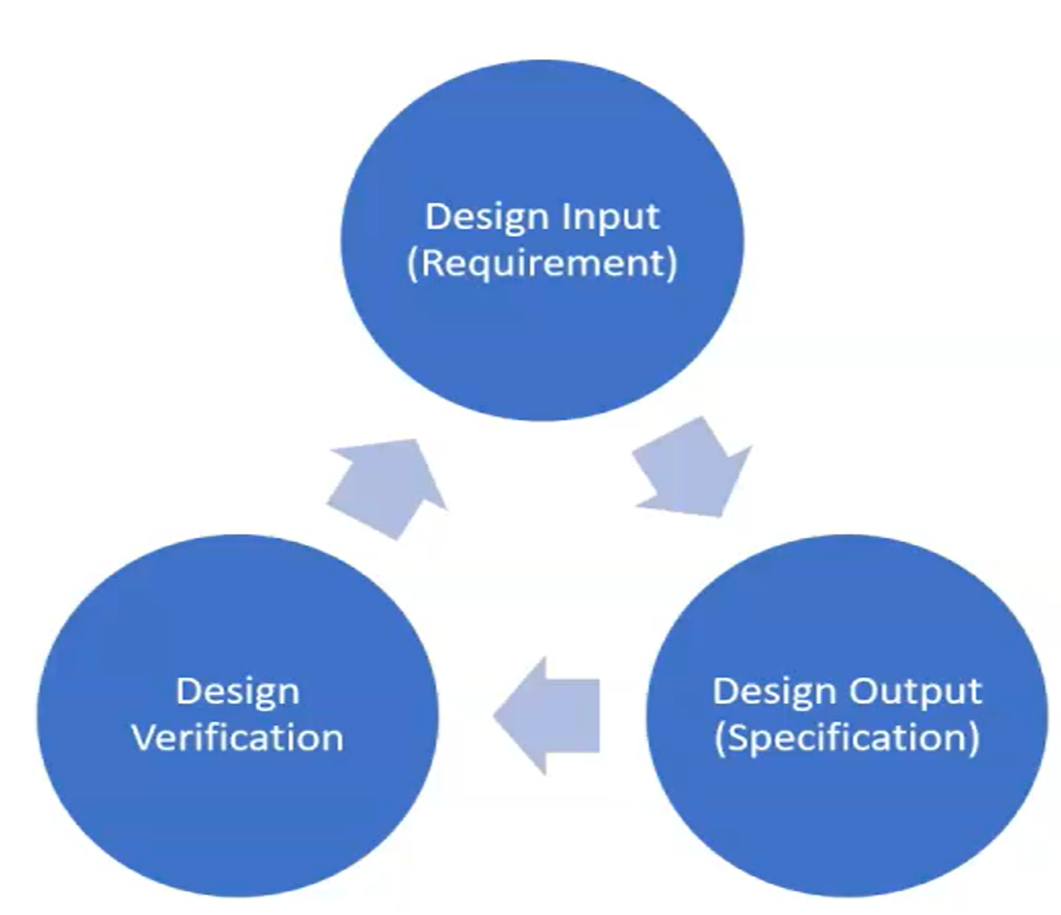
Section 7.3.6 “Design and development verification shall be performed in accordance with planned and documented arrangements to ensure that the design and development outputs have met the design and development input requirements” We should prove output=input? “The organization shall document verification plans that include methods, acceptance criteria and, as appropriate, statistical techniques with rationale for sample size” “Records of the results and conclusions of the verification and necessary actions shall be maintained”
- Design output is an input to verification plan
 Design input should include acceptance criteria with clear, verifiable and concise. Like it should be that number within 100 random units of test and all must pass the test.
verify it with authorized organizations standards! Like F2942/ISO 25539
Verification is comparing a product characteristics against a standard
Design input should include acceptance criteria with clear, verifiable and concise. Like it should be that number within 100 random units of test and all must pass the test.
verify it with authorized organizations standards! Like F2942/ISO 25539
Verification is comparing a product characteristics against a standard
ISO 17025 testing and calibration laboratories verification tests should be performed in a verified lab
- Accelerated life test is mandatory for sterilization
- Vibration
- cyclic loading
- mechanical, electromagnetic or thermal
- static loading
- humidity and temperature
- environmental chambers
- cleaning and sterilization
- especially for reusable invasive medical device
- surface finish quality
- commercial optical microscopes
- scanning electron microscope for sub um levels
- In vitro means outside of body while In vivo means inside of body
Calibration of equipments
It is necessary in product test verification Labs should be cerfified to quality management standard → ISO 17025
Validation Validation of Medical Device
Chapter 7.3.7 “Design and development validation shall be performed in accordance with planned and documented arrangements to ensure that the resulting product is capable of meeting the requirements for the specified application of intended use” “The organization shall document validation plans that include methods, acceptance criteria and, as appropriate, statistical techniques with rationale for sample size” “Validation shall be completed prior to release for use of the product to the customer” “Records of the results and conclusion of validation and necessary actions shall be maintained”
Traceability of Validation
validation answer to that question: did we design correct medical device? did we meet intended use? validation is final proof that medical design functions correctly
You have to do clinical trials for class 3 devices.
method = clinical test, animal test or simulated test
Clinical Trials
Validation means device is safe to use, does what it suppose to do and meet clinical requirements
In EU all class 3 and class 2b implantable devices must have clinical trials as validation. Clinical trials are expensive, regulated and need permission. Prospective Studies and retrospective studies. ISO 14155: Clinical investigation of medical devices for human subjects EU MedDev 2.7.1 and FDA Design Control Literature review!
EU named Validation as “Clinical evaluation” Clinical Evaluation of Medical Device
Design & Development Transfer
section 7.3.8 “The organization shall document procedures for transfer of design and development outputs to manufacturing” Output is the records to manufacture the device (DMR) Device Master Record of Medical Device in USA, Technical File of Medical Device in EU
- Inspection procedures
- Installation and service procedures
- Supplier is also important detail in Design Transfer. They have to have a valid QMS
- Needs to consider (DHR) Device History Record of Medical Device
- Design transfer needs to have proof of both Verification and Validation
Control of Design and Development Changes
Section 7.3.9 “The organization shall document procedures for control design and development changes” They should be body in company that acts as gatekeeper, authority to ask questions. design changes should be reviewed, verified, validated and approved Review should inlcude evaluation of the effect of the change. Any change to should shall be recorded.
If something bad happens with small and minor design update without proper documentation and testing, head of quality control can go to jail, head of research and development as well. CEO is already fucked up!
Design and Development Files
Section 7.3.10 “The organization shall maintain a design and developent file for each medical device type or medical device family” “This file shall include, or reference records generated to demonstrate conformity to the requirements for design and development and records for design and development changes”
Technical File of Medical Device in EU has 2 corresponding file type in US: (DHR) Device History Record of Medical Device and (DMR) Device Master Record of Medical Device
(DHF) Design History File of Medical Device
from FDA: “means a compilation of records which describes the design history of a finished device” It is living document. Even cost savings should be documented here. It should contain:
- Design Input
- Design Output
- D&D Plans
- Deliverables
- V&V records
- Design reviews
- Proces validation
- Reference to Controlled Design Documents
- Change control records
(DMR) Device Master Record of Medical Device
from FDA: “means a compilation of records containing procedures and specs for a finished device”
- Product identification
- Product description
- Revision history
- Shelf life
- Quantity of units to ship It should contain:
- Bill of Materials
- Part numbers
- Drawings
- Reference manufacturing procedures
- Test procedures
- Fixtures
- Packaging
(DHR) Device History Record of Medical Device
It must be included in (DMR) Device Master Record of Medical Device from FDA ” means a compilation of records containing the production history of finished device” issue parts, assemble part, inspect DHR should include
-
When you manufactured
-
When each product step was manufactured
-
Quantity of it
-
Label check
-
Part number
-
work order number
-
sequence of steps
-
initial of the employee each step
-
rework orders
-
non-conformances
-
testing
-
shipping record
Manufacture need it to evaluate, trace, follow trends of quality within variances.
So, it is a record that the production of the device occured. It can be named as Router?
Technical File of Medical Device
Collection of documents required by (MDR) Medical Device Regulation of EU It has sections:
- Device description
- Product description
- list of accesories
- regulatory approval
- classification
- Labels & Packaging
- Design & Manufacturing Information
- (GSPR) General Safety Performance Requirements
- Benefit-Risk Analysis and risk management
- ISO 14971
- Post market surveillance
- Clinical experience feedback
- Product verification and validation
- Verification
- Chemical, physical or biological tests
- In-house testing
- CTQ acceptance criteria
- Sample size, calibration
- test method validation
- Bench testing
- Statistical Analysis
- Categorization
- ISO 10933 what test need to be done
- Microbiological Safety & Animal origin issue
- Coated devices has their own tests
- biocompatibility
- Validation
- Applies to Class 3 and 2b
- Verification
- Post market surveillance
- Ongoing process
- Feed backs into Technical documentation
In EU once you are done, Declaration of Conformity: declare that all items in the technical file has been completed.